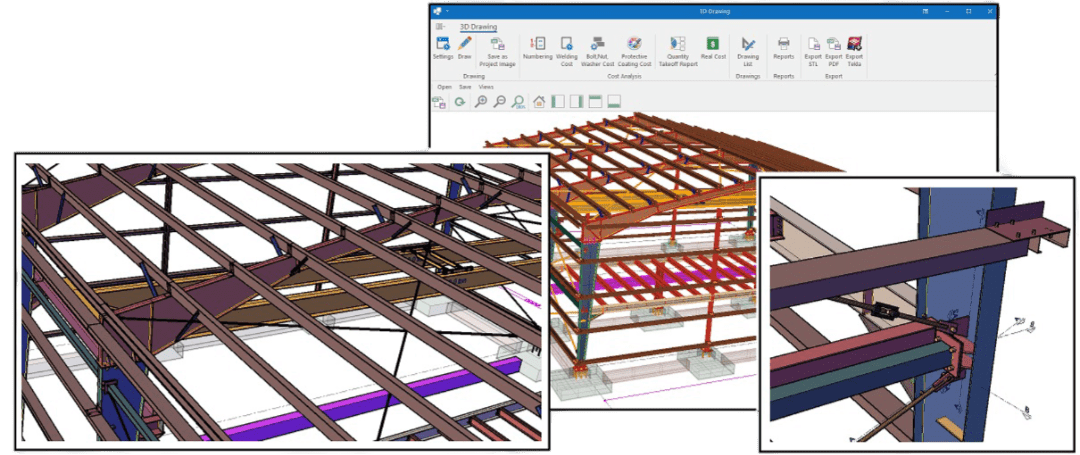
MkaPEB Design Codes
The main purpose of MkaPEB is to enable the engineer to reach the lowest cost solution in the shortest time without compromising on quality.
MkaPEB is one of the most efficient and comprehensive software ever developed for single-storey steel structures in the world. It has many unique features that prevent users from making mistakes.
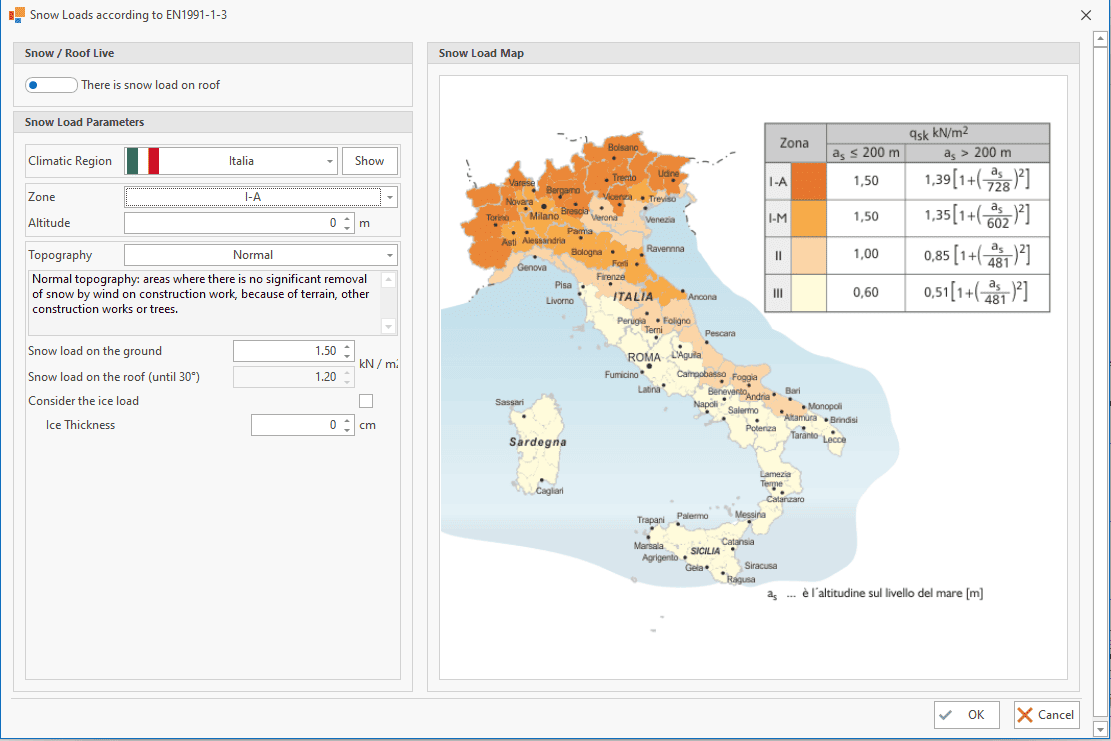
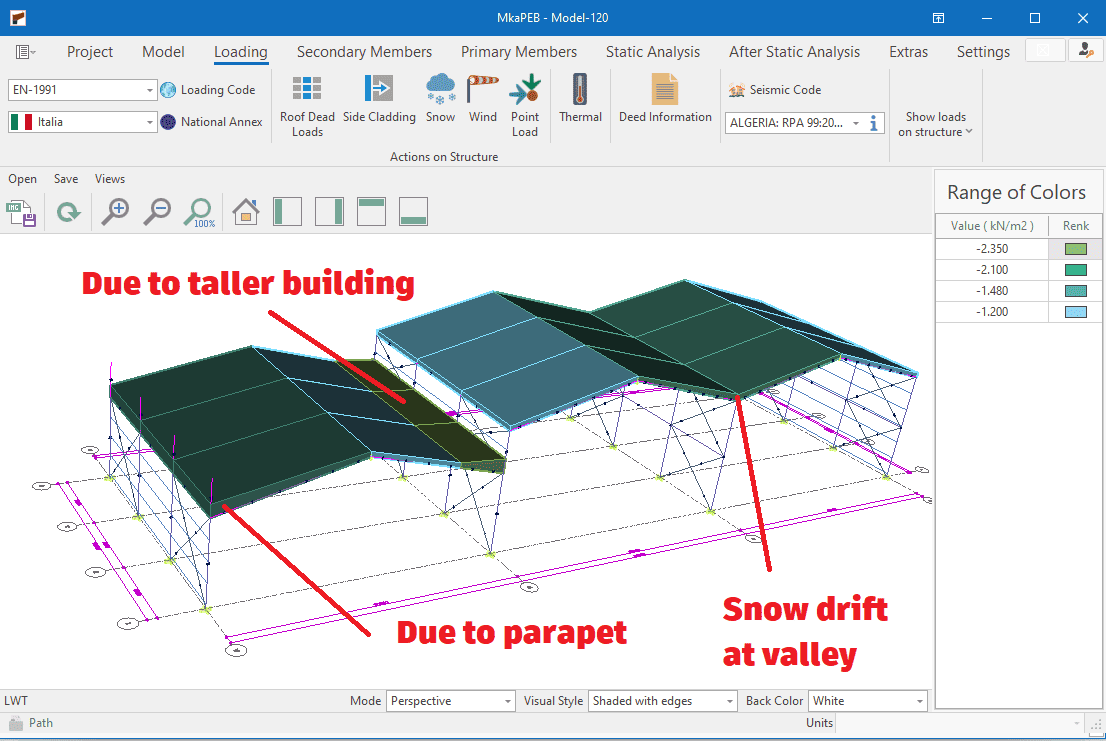
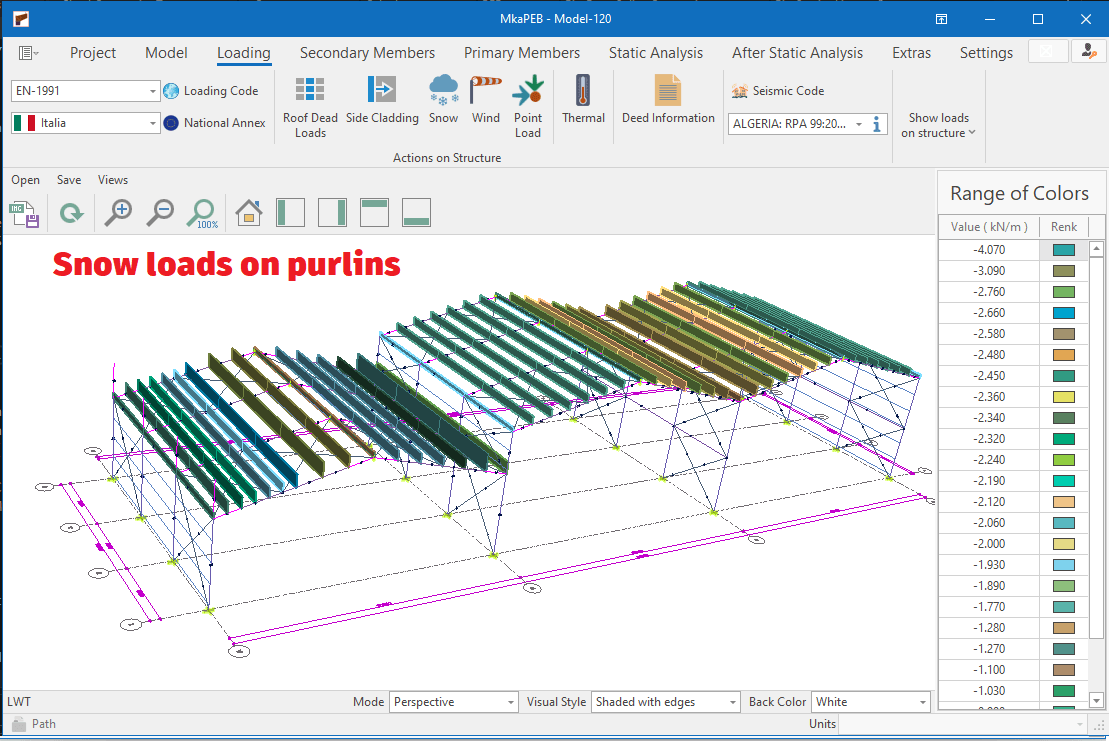
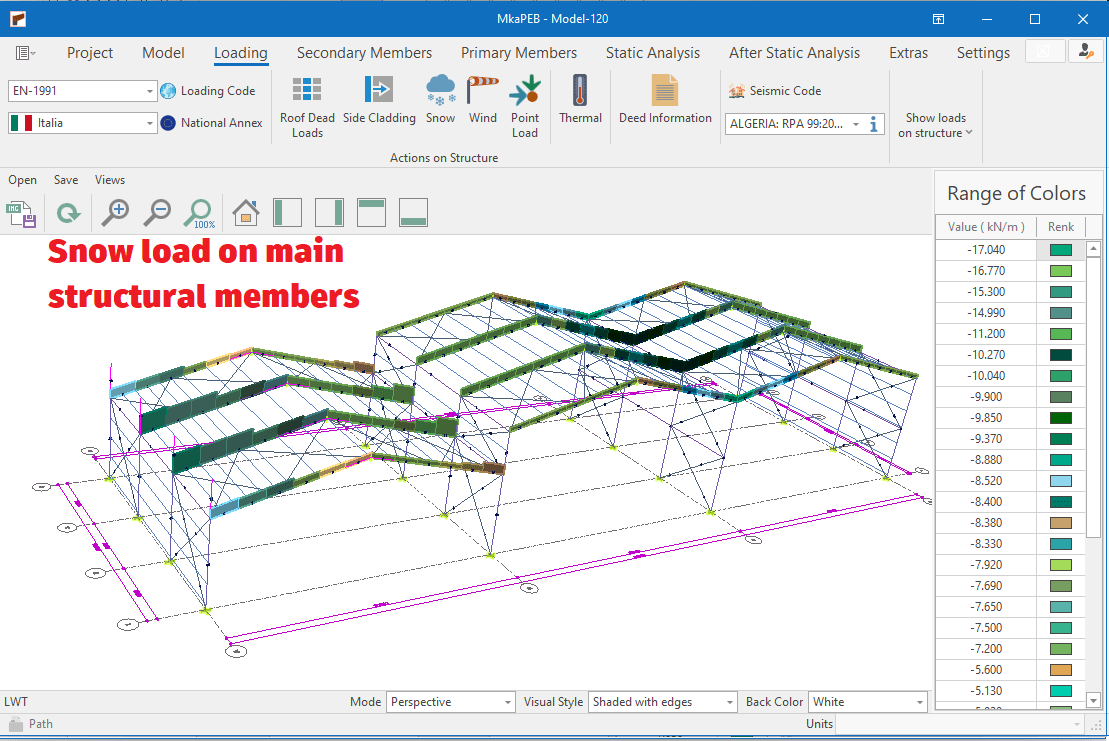
Snow Load Generation
The following standards are available:
⦿ EN 1991 - 1 - 3 (incl. National Annexes)
⦿ ASCE - 07 - 16
⦿ IS - 875 - 2015
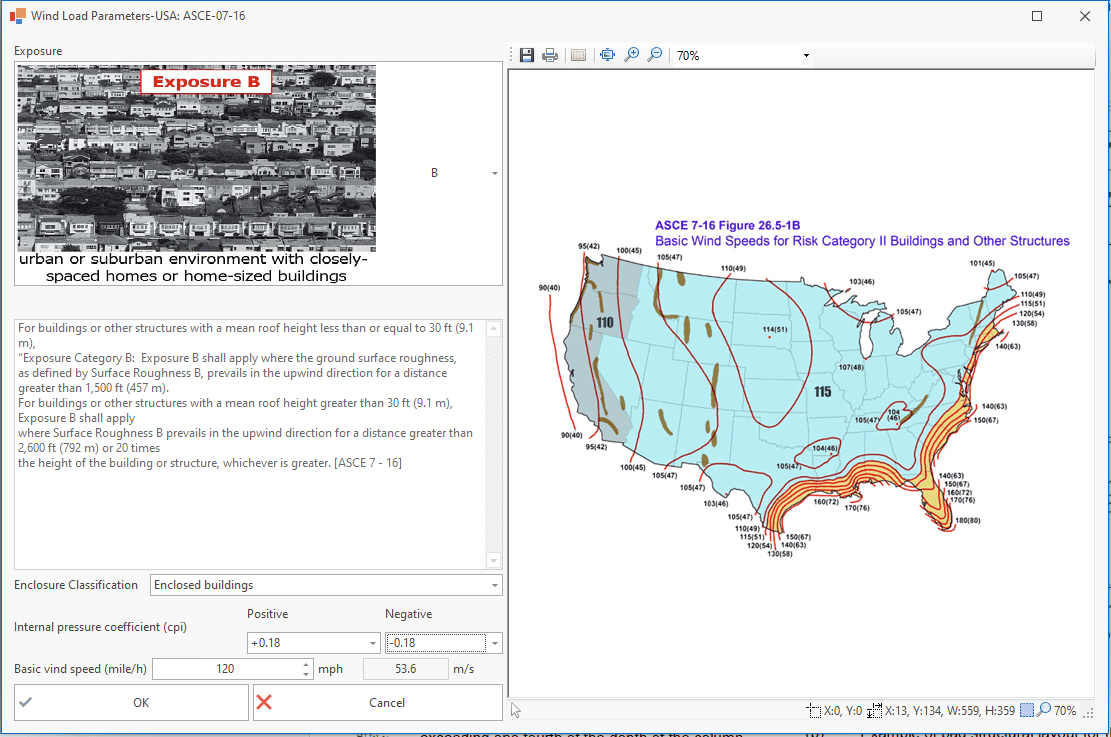
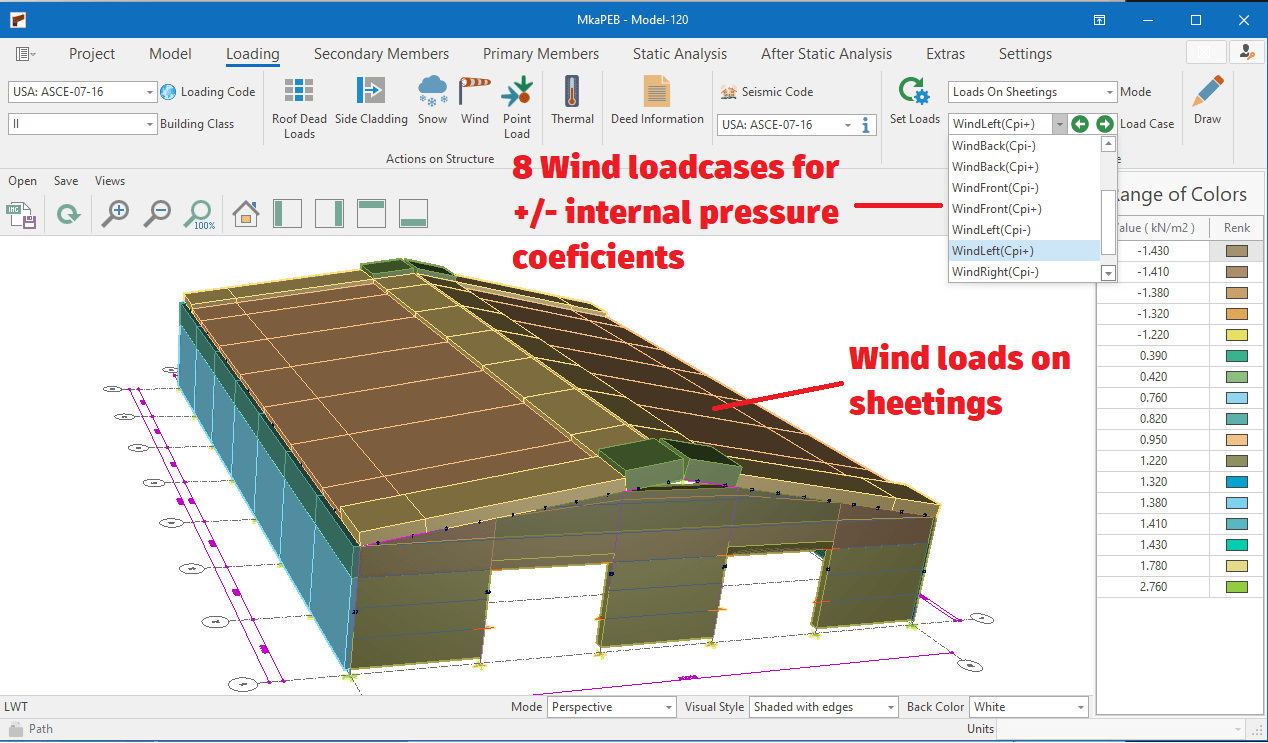
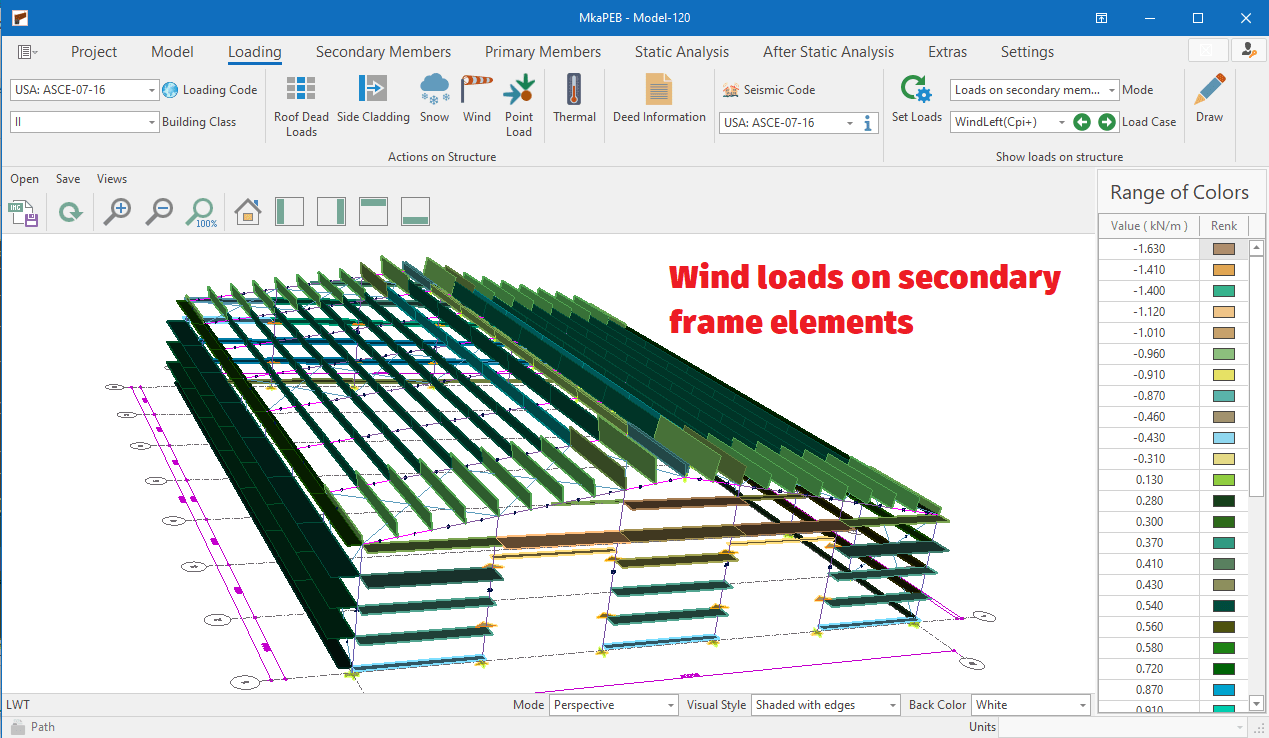
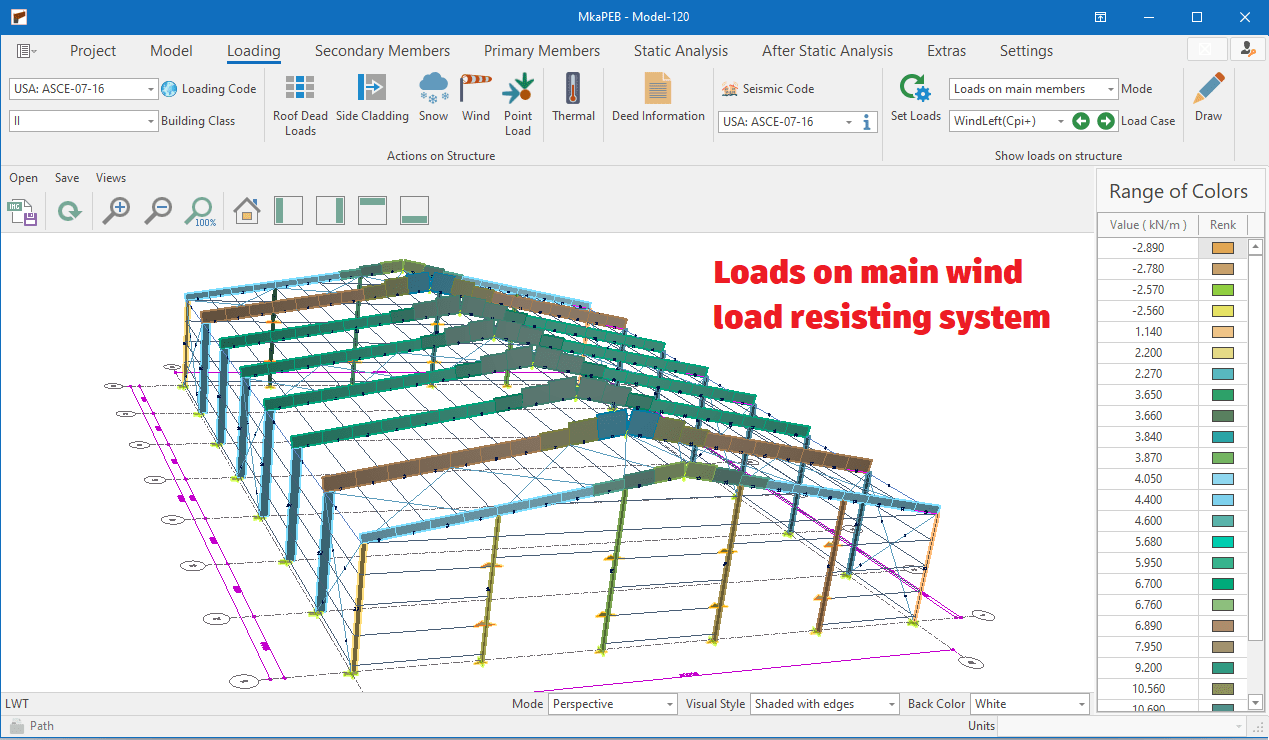
Wind Load Generation
The following standards are available:
⦿ EN 1991 - 1 - 4 (incl. National Annexes)
⦿ ASCE - 07 - 16
⦿ IS - 875 - 2015
For snow and wind loads according to European Standards, the following National Annexes are available
| ⦿ Austria, | ⦿ Greece, | ⦿ Russia, |
| ⦿ Belgium, | ⦿ Iceland, | ⦿ Singapore |
| ⦿ Bulgaria, | ⦿ Ireland, | ⦿ Slovakia, |
| ⦿ Croatia, | ⦿ Italia, | ⦿ Slovenia, |
| ⦿ Cyprus, | ⦿ Malaysia, | ⦿ South Africa, |
| ⦿ Czech Republic, | ⦿ Netherlands, | ⦿ Spain, |
| ⦿ Denmark, | ⦿ Norway, | ⦿ Sweden, |
| ⦿ Finland, | ⦿ Poland, | ⦿ Türkiye |
| ⦿ France, | ⦿ Portugal, | ⦿ United Kingdom |
| ⦿ Germany, | ⦿ Romania, |
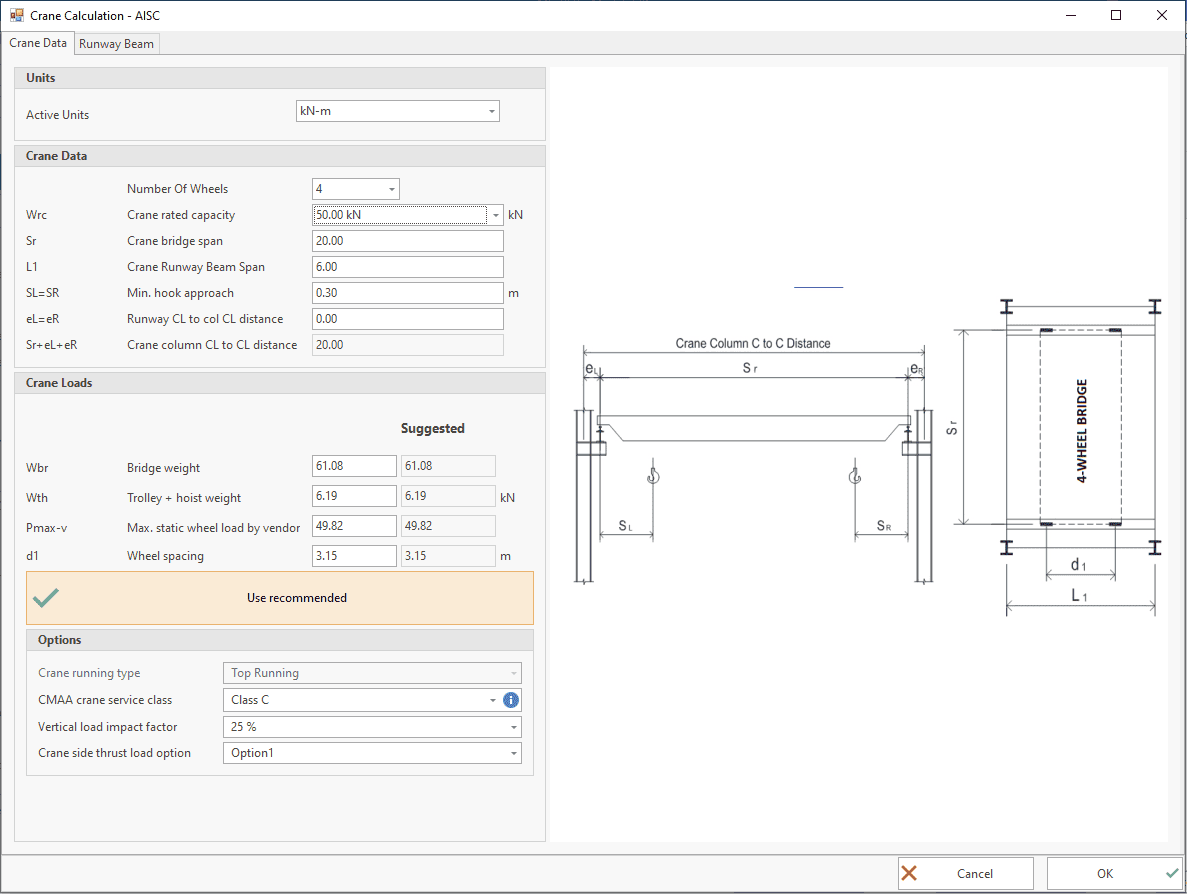
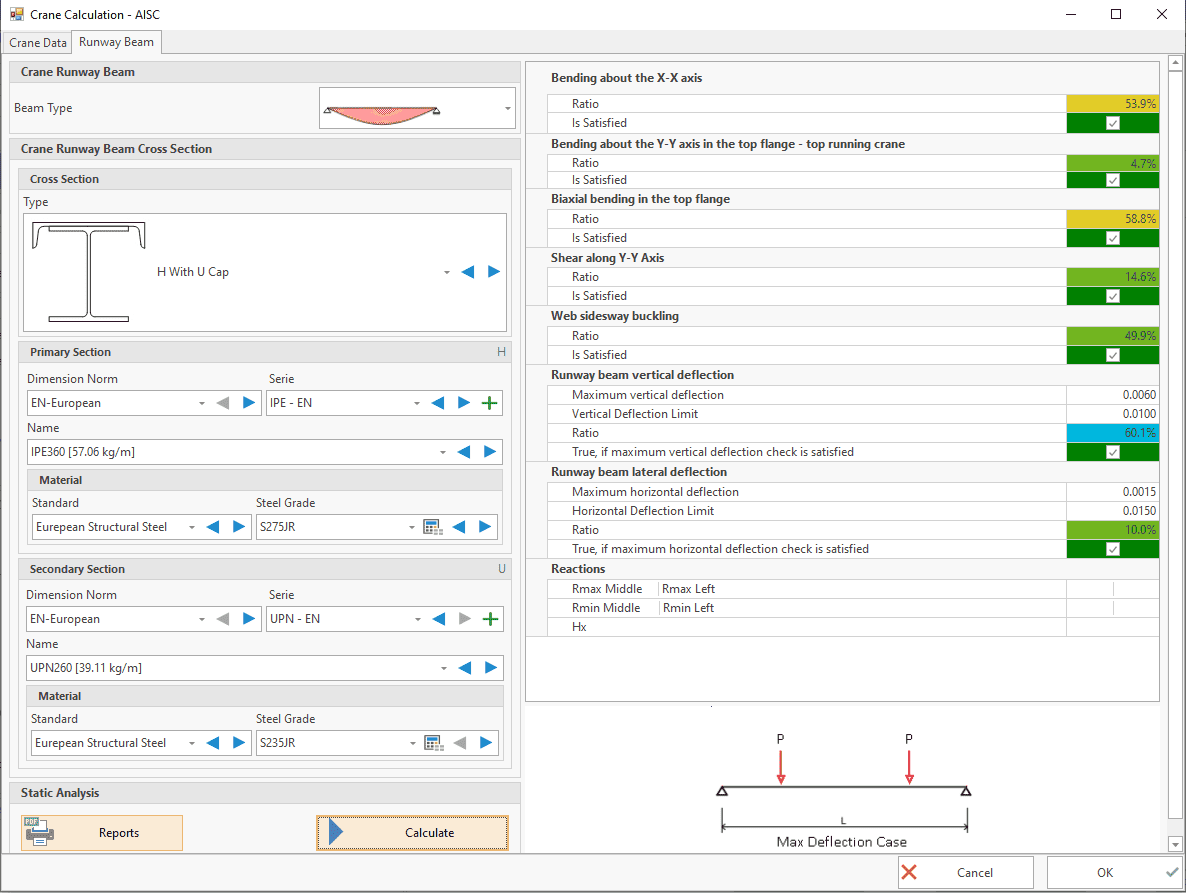
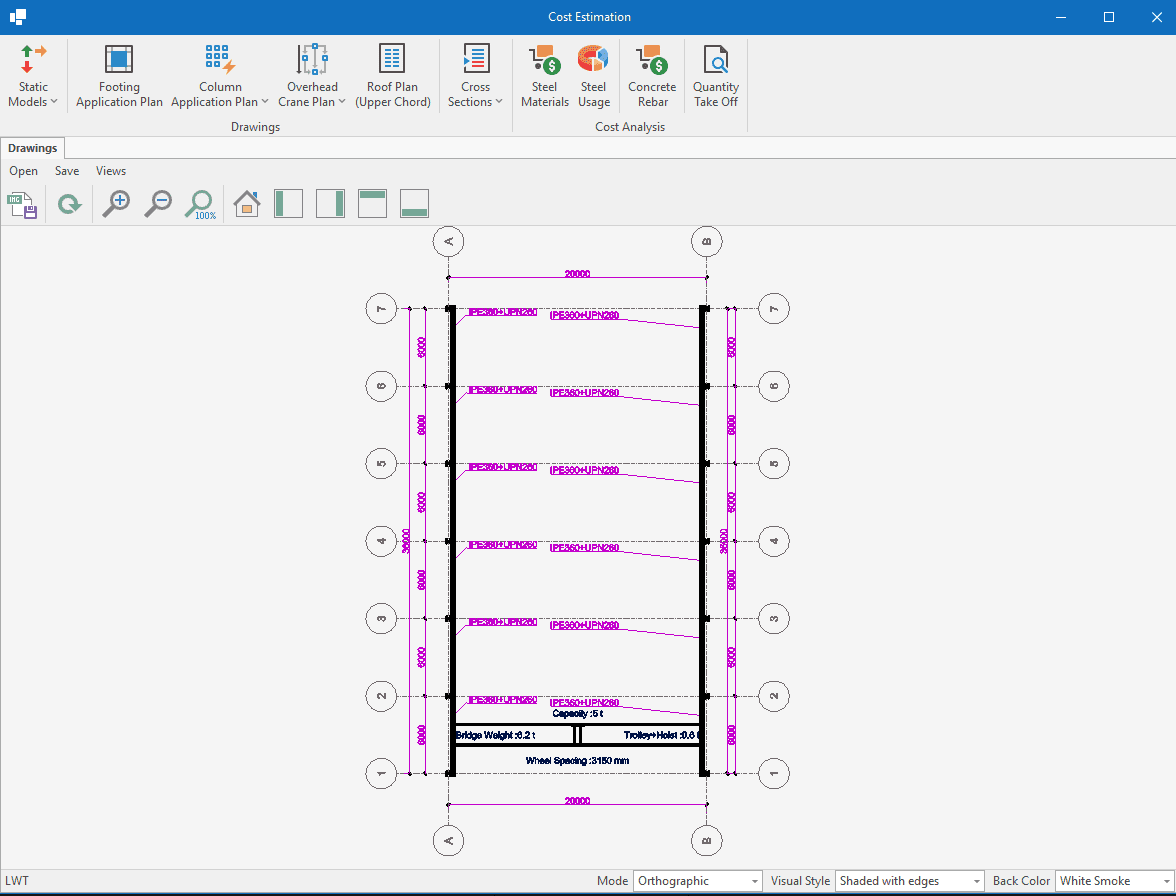
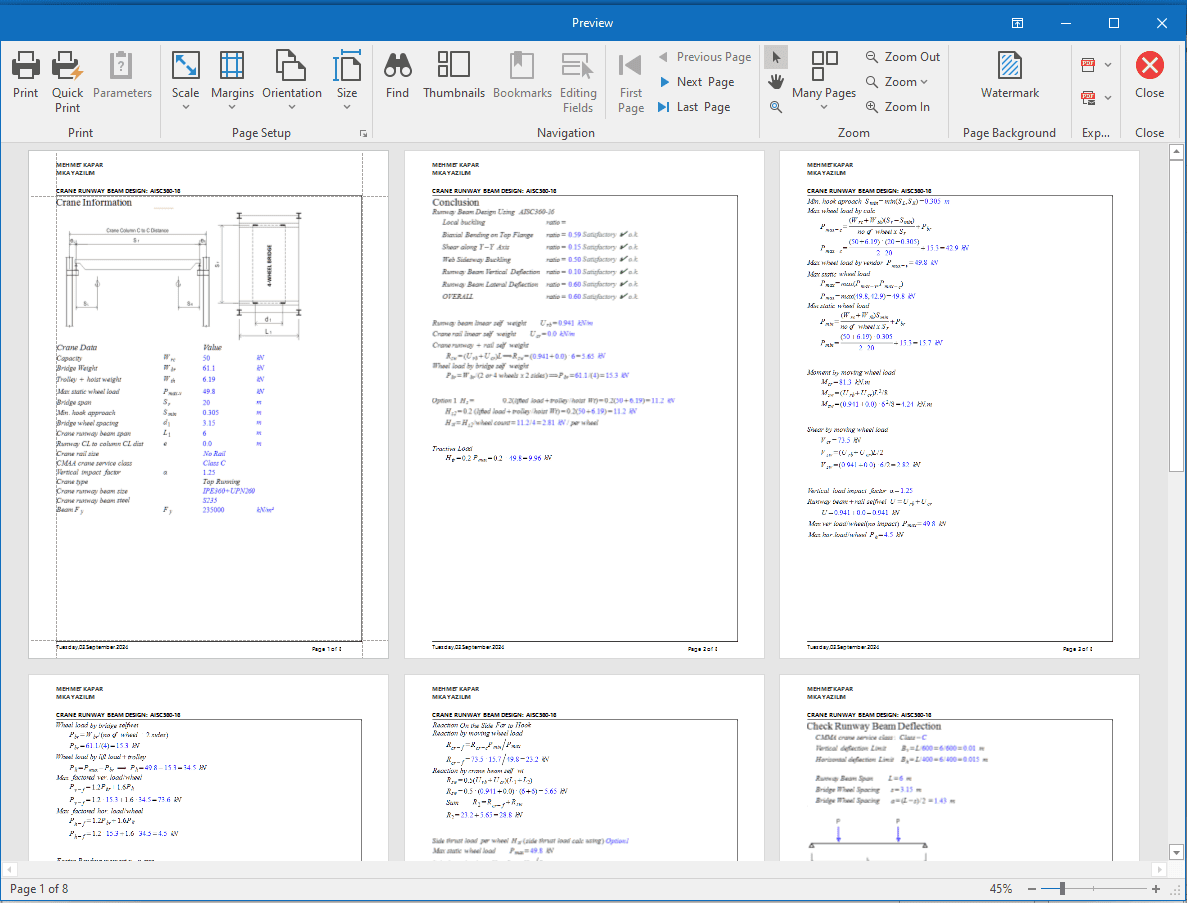
Overhead Crane Loads
The following standards are available:
⦿ EN 1991 - 3
⦿ AISC Design Guide 7
Seismic codes in MkaPEB according to continents
Europe
⦿ |
Eurocode 8 |
Included National Annexes |
|||
|
|||||
⦿ |
TEC-2018 |
Turkish Building Earthquake Code |
|||
⦿ |
EAK-2000 |
Greek Code for Seismic Resistant Structures |
|||
⦿ |
P100-1/2013 |
Romania Code for Earthquake Resistant Design |
Asia
⦿ |
IS 1893 : 2016 |
Indian Standard: Criteria for Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures |
⦿ |
GB50011: 2010 |
Chineese Standard: Code for Seismic Design of Buildings |
⦿ |
SBC-301: 2016 |
Saudi Arabia: Seismic Provisions in the Saudi Building Code |
⦿ |
DUBAI: 2013 |
United Arab Emirates: Seismic Design Code For Dubai, Dubai Municipality |
⦿ |
BNBC: 2020 |
Seismic Provisions in the Bangladesh National Building Code |
⦿ |
BCP: 2021 |
Seismic Provisions in the Building Code of Pakistan |
⦿ |
NSCP: 2010 |
Seismic Provisions in the National Structural Code of the Philippines |
⦿ |
SI-413: 2019 |
Israeli Standard: Design of Structures for Earthquake Resistance |
⦿ |
TAIWAN:2019 |
Seismic Force Requirements for Buildings in Taiwan |
⦿ |
MALAYSIA: EC-8 NA |
Malaysia National Annex to MS EN 1998 |
⦿ |
SINGAPORE:EC-8 NA |
Singapore National Annex to SS EN 1998 |
⦿ |
TCXDVN 375-2006 |
Vietnamese Earthquake Design Code (Based on EN-1998) |
America
⦿ |
ASCE/SEI 7-16 |
USA Standard: Minimum Design Loads For Buildings And Other Structures |
⦿ |
ANSI/AISC 341-16 |
USA Standard: Seismic Provisions for Structural Steel Buildings |
⦿ |
NBCC-2020 |
Canada: Seismic Provisions in the National Building Code of Canada |
⦿ |
INPRESS-CIRCOS-103 |
Argentinean Standards for Earthquake Resistant Constructions |
⦿ |
NDBS: 2006 |
Bolivia: Norma Boliviana de Diseño Sísmico (2006) |
⦿ |
NCH433: 2012 |
Chile: Chilean seismic code |
⦿ |
NSR-10 |
Colombia: Reglamento colombiano de construcción sismo resistente |
⦿ |
CRSC- 2010 |
Costa Rica: Código sísmico de Costa Rica 2010 |
⦿ |
MOC-2008 |
Mexico: Normas Técnicas Complementarias para Diseño por Sismo |
Africa
⦿ |
ECP‑201: 2012 |
Egyptian Code of Practice for Calculation of Loads and Forces in Structures and Buildings (Based on EN-1998) |
⦿ |
RPA-99: 2003 |
Algerian Earthquake Resistant Regulations |
⦿ |
RPS-2011 |
Morocco: D’utilisation Du Reglement De Construction Parasismique |
⦿ |
SANS-10163-4 |
South Africa: Seismic actions and general requirements for buildings (Based on EN-1998) |
Australia
Our work on earthquake actions AS-11704-2007 in Australia continues. It is expected to be finalised in the next few months.
ANSI/AISC-360-16 |
|
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings |
EN-1993-1-1 (2005) |
|
Eurocode 3. Design of steel structures General rules and rules for buildings |
IS-800 (2007) |
|
Indian Standard: General Construction in Steel Code of Practice |
CYTHYE-2016 (Turkiye) |
|
Turkish Standard: 2016 Regulation on Design, Calculation and Construction Principles of Steel Structures |
EN-1993-1-3 |
|
Eurocode 3. Design of steel structures - General rules Supplementary rules for cold-formed members and sheeting |
ACI-318-14 |
|
Building Code Requirements for Structural Concrete. |
EN-1992-1-1 |
|
Eurocode 2: Design of concrete structures - Part 1-1 General rules and rules for buildings |
TS-500: 2000 |
|
Turkish Standard: Requirements for Design and Construction of Reinforced Concrete Structures |
AISC-360-16 & Design Guides |
| Specification for Structural Steel Buildings |
EN-1993-1-8 |
|
Eurocode 3: Design of steel structures - Part 1-8 Design of joints |